Automobile Transmission System
Key Highlights
-
Explanation of what an automobile transmission system is.
-
Detailed breakdown of components, types, and functions.
-
How a transmission system works and what happens inside.
-
Requirements for an efficient system.
-
Comparison of various types (manual, automatic, etc.).
-
Advantages, disadvantages, and modern advancements.
-
Maintenance guidelines and FAQs.
-
Historical context and relevance in competitive exams.
What Is a Transmission System in Automobiles?
The transmission system in automobiles is a vital component of any vehicle. It acts as the bridge between the engine's power and the wheels that drive the vehicle forward. This system enables seamless control over the speed and direction of the automobile, allowing it to navigate various road conditions and terrains. It has evolved significantly over the years—from early manual systems to advanced automatic and continuously variable transmissions—enhancing driving comfort, fuel efficiency, and overall performance.
This discussion will clear all your doubts regarding the automobile transmission system. This topic is also significant for mechanical engineering students and for competitive exams such as SSC JE ME and RRB JE.
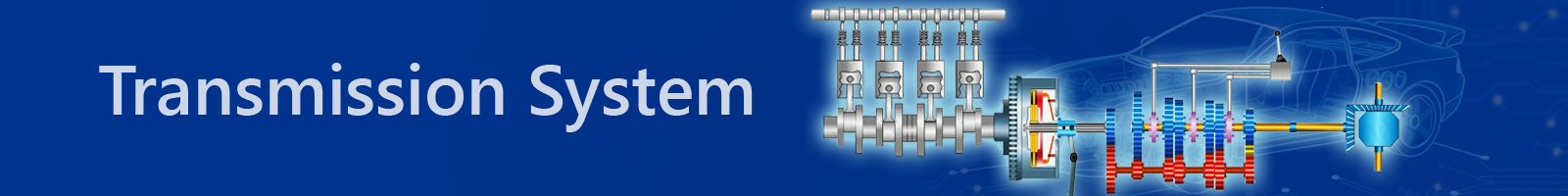
Components of Transmission System in Automobiles
The transmission system comprises several essential components that ensure the vehicle operates efficiently by transmitting engine power to the wheels.
Major Components:
-
Clutch – Engages and disengages engine power smoothly.
-
Gearbox – Offers various gear ratios for different conditions.
-
Propeller Shaft – Connects gearbox to the differential.
-
Differential – Allows wheels to rotate at different speeds.
-
Live Axle – Transfers motion to the wheels.
These components work together to provide optimal vehicle control, power transmission, and comfort.
Functions of the Automobile Transmission System
-
Transmits power from engine to wheels.
-
Facilitates gear shifting.
-
Enables vehicle to move from a stationary position.
-
Enhances torque when required (e.g., during hill climbs).
-
Allows reverse movement.
-
Permits smooth acceleration and deceleration.
-
Maintains engine performance and fuel economy.
Working of Transmission System in Automobiles
-
The engine generates rotational power via the crankshaft.
-
The clutch engages/disengages the engine from the transmission system.
-
The gearbox converts engine speed into usable torque.
-
The propeller shaft transmits the torque to the differential.
-
The differential splits torque between the drive wheels.
-
The live axle ensures motion is passed to the wheels efficiently.
The system adjusts gear ratios to adapt to road conditions, ensuring performance, comfort, and safety.
Requirements for a Good Transmission System
-
Smooth gear engagement/disengagement.
-
Ability to vary torque/speed as needed.
-
Efficient transfer of power.
-
Capability to redirect motion.
-
Synchronization during turns.
-
Flexibility for axle movements on uneven terrain.
Types of Transmission Systems in Automobiles
1. Manual Transmission
-
Driver manually selects gears using a clutch and gear lever.
-
Offers greater control but requires skill.
2. Automatic Transmission
-
Uses torque converters and planetary gearsets.
-
Automatically shifts gears based on speed/load.
-
Ideal for urban traffic and ease of driving.
3. Semi-Automatic Transmission
Blends manual control with automatic ease.
a) Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT)
-
Two clutches handle odd and even gears for seamless shifts.
b) Sequential Transmission
-
Gears are shifted sequentially (used in racing and motorcycles).
4. Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT)
-
Uses belt and pulley system.
-
No fixed gear ratios.
-
Known for fuel efficiency and smooth acceleration.
Modern Transmission Systems
-
Electronic Control Units (ECUs) for intelligent gear shifting.
-
Tiptronic and Paddle Shifters in high-end cars.
-
Hybrid Transmission Systems in electric vehicles.
Advantages of Transmission Systems
-
Improved fuel economy.
-
Smoother acceleration.
-
Enhanced control over vehicle dynamics.
-
Better adaptability to different terrains.
Disadvantages of Transmission Systems
-
Manual systems require driver expertise.
-
Automatic systems are costlier and complex.
-
Regular maintenance required.
Maintenance Guidelines
-
Regularly check transmission fluid.
-
Replace clutch plates as needed.
-
Inspect gearbox for unusual noises.
-
Service differentials periodically.
-
Monitor and address leaks promptly.
History of Transmission Systems
Early automobiles used simple direct-drive systems. The first manual gearboxes appeared in the early 1900s. Over the decades, innovations led to the development of synchromesh gearboxes, automatic transmissions in the 1940s, and eventually the advent of CVTs and electronic transmissions in modern cars.
FAQs About Automobile Transmission Systems
Q1: What is the primary function of a transmission system? A: To transfer power from the engine to the wheels while allowing speed and torque variations.
Q2: Which transmission is more fuel-efficient? A: CVTs and well-tuned manuals generally offer better fuel economy.
Q3: What is the role of the clutch? A: To smoothly engage or disengage the engine from the transmission system.
Q4: How long does a transmission last? A: With proper maintenance, it can last 100,000 to 200,000 km or more.
Conclusion
The automobile transmission system is the heart of vehicle mobility. From transferring power to ensuring smooth and safe driving, it plays a critical role in performance and efficiency. Understanding its components, types, and operations helps in better maintenance and enhances technical knowledge—essential for engineers and car enthusiasts alike.